Visual thinking is a new methodology based on synthesising and explaining through images, that is, visualising the complicated and transforming it into something digestible, referring to the proverb “a picture is worth a thousand words”.
In an increasingly complex world, where the amount of information literally grows by the minute, data saturation leads to a state of infoxication in which our limited mind is not able to process any more. It is therefore necessary to have new strategies or ways of thinking that help us to better synthesise this information.
The importance of visual thinking
Although visual thinking may sound like something new and innovative, the truth is that the image is expression itself, the most basic form of human communication since the beginning of time. Since we were children, just like our prehistoric ancestors in the caves, without knowing how to express ourselves through language, the way we had to express our thoughts was through drawing; a language that, like love, is universal; As Albert Einstein said: “if it cannot be drawn, it does not exist”.
Visual thinking is a vital skill for developing new ideas and designs, communicating those ideas effectively and collaborating with others to make them a reality.
¿What is visual thinking?
Being one of the most powerful techniques with the highest capacity for information retention, visual thinking helps to understand the patterns or ideas that underlie the background; If you are able to draw it, you have understood it.
However, this methodology has to be combined with others, otherwise we would be living in a kind of Pictionary, since we have not been visually capturing information all our lives.
Visual thinking: it is our natural way of thinking
The success of this new methodology lies in the fact that human beings, however many communication codes have been created, think naturally with images (although we will go over verbal thinking later). In this way, the memorisation of information is multiplied compared to what we transmit with words alone. Let’s take a look at what else visual thinking has to offer.
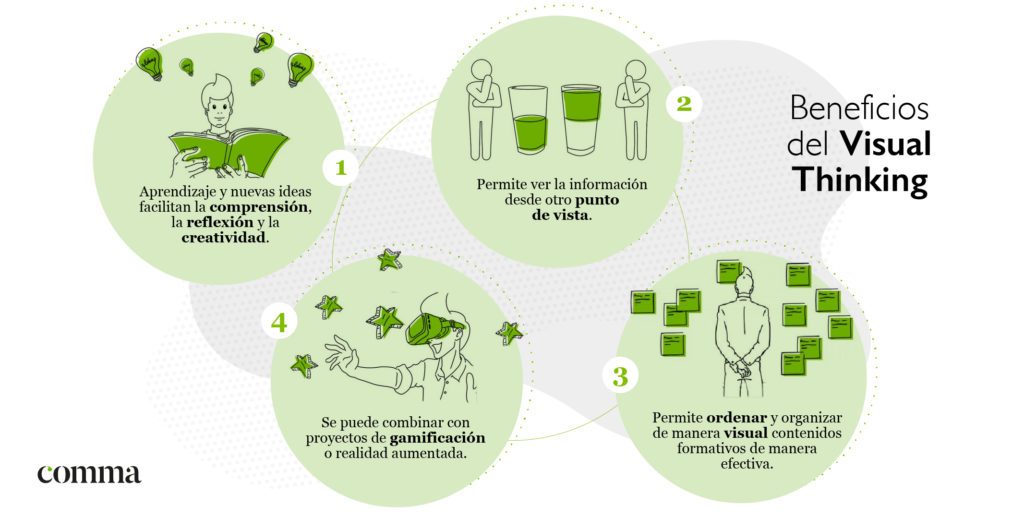
Advantages of visual thinking
- Stimulates creative thinking: Visual thinking encourages the generation of innovative ideas by allowing different perspectives to be explored and concepts to be connected visually; The graphical representation of information facilitates the association of ideas and the discovery of new relationships between concepts, which encourages creativity.
- Broadens understanding: By using pictures, diagrams and diagrams to represent ideas and concepts, Visual Thinking helps to better understand information. Visual representations allow a holistic view of issues, facilitating the identification of patterns, capturing key concepts and understanding the relationship between them.
- Change of perspective: Visual Thinking provides the ability to see information from different points of view. By graphically representing concepts and relationships, multiple approaches can be explored and the understanding of a topic can be enriched. This promotes cognitive flexibility and openness to new ideas and solutions.
- Integration with gamification and augmented reality: Visual Thinking can be combined with gamification or augmented reality projects to make learning more interactive and engaging; Through the use of visual elements and the active participation of the learner, a more dynamic and motivating learning environment is created.
- Effective organisation of training content: Visual Thinking allows to order and organise training contents in a visually structured and effective way; Through the creation of mind maps, diagrams, infographics or other visual resources, the navigation and understanding of information is facilitated, turning complex concepts into more accessible and clear visual representations.
Differences between visual and verbal thinking
People who think visually use mental imagery on a conscious level to plan, solve problems or simply use their imagination. What is interesting, however, is that many people are not aware that not everyone thinks like them.
While there are many nuances, there are essentially two types of thinkers: visual and verbal; What are the most important differences between the two?
Visual thinkers
- They think about the information by seeing images in their head (a bit like watching a film).
- People who use visual thinking experience abstract thoughts that sometimes need to be verbalised before they can be fully formed.
- Visual thinkers often need some time to answer a question or find the right word or phrase to express what they are thinking.
Verbal thinkers
- They think of information in words (like talking to themselves).
- They experience an internal narrative or monologue that unfolds in sentences they hear in their head.
- They often need to close multiple verbal threads before they can turn their full attention to new information.
Some examples of visual thinking
At comma we are committed to new methodologies to help organisations achieve their objectives. In addition to the use of design thinking, it is also common for our design team to create pieces in which visual thinking takes centre stage.
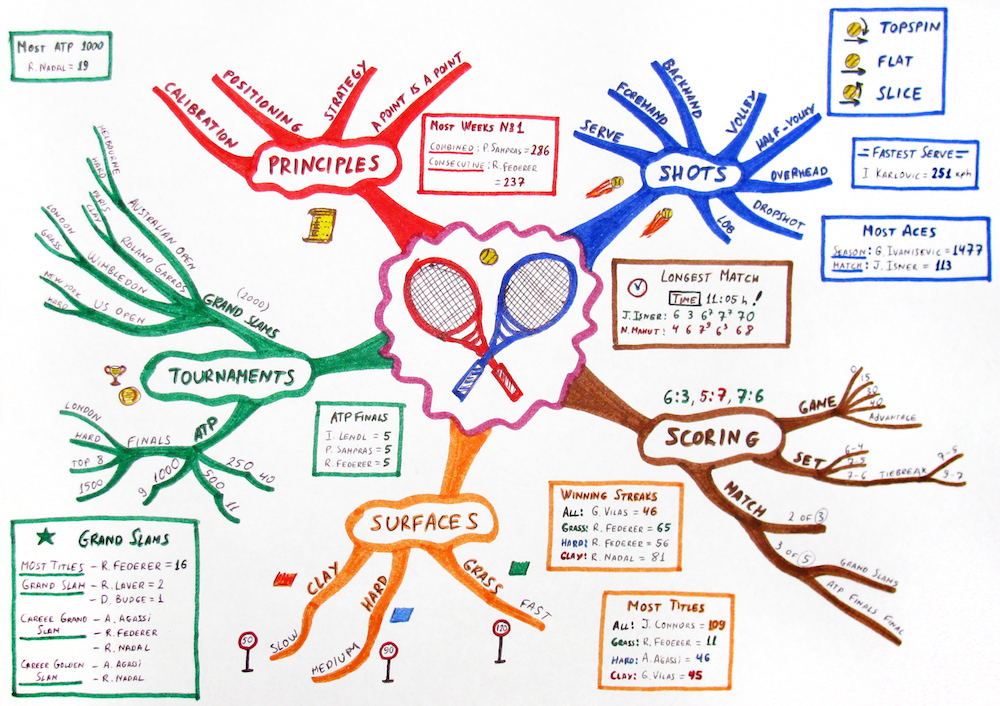
In this sense, one of the most common formats used in the visual thinking is infographics, a piece that mixes images and text to show information in a simple, attractive and easy-to-understand way.
In these examples made by comma’s Design and Creativity team you can see some examples of visual thinking that we have executed for our clients. These infographics allow you to acquire information quickly, as the information is presented in a synthesised way and in a very attractive format.
Applications of visual thinking in education
Visual thinking can be very useful in the classroom to develop certain skills:
- Learning to learn
- Communication competence
- Digital competence.
In addition, visual thinking is helpful in developing skills such as critical and creative thinking. In short, this methodology is ideal if our intention is for students to be able to analyse, reflect and communicate appropriately.
On the other hand, from the Inspiratics blog, they state that “visual thinking has great potential in the educational environment, where it is adouble benefit. On the one hand, the study content is presented in an attractive way, which increases student interest and attention. And, on the other hand, by making their own graphical representations of the content, a slower but more effective learning process is initiated. This is because when translating textual content into drawings or vice versa, skills such as filtering, managing and spatial organisation of the content to be learned.”
All this can be seen in the course Visual Thinking in Education, a video training proposal created by the National Institute of Educational Technologies and Teacher Training (INTEF).
Business applications of visual thinking
Visual Thinking is a powerful tool that is increasingly used in business environments to communicate ideas, facilitate collaboration and solve problems visually. Here are some examples:
Troubleshooting
Visual Thinking is used to visually represent the challenges and obstacles a company faces. Through diagrams, mind maps or illustrations, teams can visualise and better understand the nature of the problem, identify its underlying causes and explore potential solutions collaboratively.
Idea generation
Visual Thinking is an effective tool for fostering creativity and idea generation in brainstorming sessions. Using techniques such as concept drawing, diagramming or visual mapping, teams can visualise and explore new ideas, associations and connections between concepts, which can lead to innovative solutions.
Strategic planning
Visual Thinking is used to visualise and communicate business vision and strategy. Strategy maps, flow charts and infographics are visual tools that help leaders and teams understand and communicate the strategic objectives, the actions needed and the relationships between different components of the strategic plan.
Presentations and communication
Visual Thinking is an effective way of communicating complex ideas in a clear and memorable way. By using graphs, pictures and diagrams in presentations, the audience’s understanding and retention of information is facilitated. In addition, the use of visual imagery can spark the interest and participation of viewers.
Product development
Visual Thinking is used in product development to visualise and communicate desired product features, functionalities and experiences. Sketches, storyboards and user experience maps are examples of visual tools used to explore and communicate design ideas, improve collaboration between multidisciplinary teams and get early feedback from clients.
Change management
Visual Thinking is used in organisational change processes to visualise and communicate the vision of change, identify expected impacts and challenges, and design action plans. Flowcharts, change maps and visual representations of processes enable teams to better understand the proposed changes and their involvement, facilitating adoption and collaboration in the change process.
Tools for using visual thinking
As we have already explained, the Visual Thinking is a versatile methodology that can be applied in a wide range of contexts, from education and business to personal development. To work effectively with Visual Thinking, there are several digital tools and applications that can facilitate and enhance this methodology. The following are some of the most common and recommended applications:
Adobe Illustrator
Adobe Illustrator is a comprehensive graphic design tool that allows you to create vector illustrations and custom graphics. It is ideal for designing diagrams, mind maps, infographics and other visual elements used in Visual Thinking.
Inkscape
Inkscape is an open source graphic design software that offers similar features to Adobe Illustrator. It is an accessible and versatile option for creating vector graphics, diagrams and other visual elements used in Visual Thinking.
Tayasui Sketches
Tayasui Sketches is a digital drawing application available for mobile devices. It provides a wide range of drawing tools and realistic brushes, making it an ideal choice for creating quick sketches and visual representations in Visual Thinking.
Prezi
Prezi is an online presentation tool that allows you to create dynamic, non-linear presentations; With Prezi, you can combine images, text and graphics to visually create powerful stories and visual narratives that support Visual Thinking;
Mindmaps
Mindmaps (also known as mental maps) are visual representations of interconnected ideas and concepts; There are several applications and tools available, such as XMind, MindMeister and Coggle, that allow you to create mind maps digitally; These applications facilitate the visual organisation of ideas and concepts in Visual Thinking;
Videoscribe
Videoscribe is an animated video creation tool that allows you to create attractive and dynamic visual presentations; It is especially useful for Visual Thinking, as it allows you to combine hand-drawn images with text and animations to explain concepts and narratives in a visually appealing way;
Piktochart
Piktochart is an online platform that allows you to create infographics in a simple and visually appealing way; It offers a wide variety of customisable templates, icons and graphics that make it easy to create informative and visually impactful infographics in Visual Thinking;
Canva
Canva is an online graphic design tool that offers a wide variety of templates and visual resources for creating custom designs; It is useful for creating presentations, infographics, diagrams and other visual elements used in Visual Thinking;
Genial.ly
Genial.ly is an interactive online design platform that allows you to create presentations, infographics, maps and other visual resources; It offers a wide range of templates and interactive elements that facilitate the creation of visually appealing content in Visual Thinking;
Visual thinking: look, see, imagine and show
Although visual thinking has been criticised, among other things, for the time it takes to put a simple concept on paper, or the fact that not everyone is gifted with a gift for drawing, we must not forget that it is one more resource that must be part of a combination of other methodologies, and that it usually includes a textual part.
- With regard to the time invested, let us remember that it is not a simple drawing, as it involves the understanding, internalisation, interpretation, organisation and graphic and personal explanation of ideas or knowledge which, once understood, we make our own.
- As far as artistic ability is concerned, with a few exceptions, most of the examples we can find are made up of a sketch with basic and simple strokes that we can all do without further complication.
Do you dare to think with drawings using visual thinking?